molar conductivity table
The molar conductance of very dilute solutions 140 10 4 mol dm 3 was measured using a digital conductometerThe viscosities of the solutions were measured with an Ubbelohde suspended bulb viscometer. Take the link to Nuclear data at the bottom of the display for any element.

Limiting Molar Conductivity K Diss And F For Polyelectrolytes Download Table
The molar electrical conductivity Λ of an electrolyte solution is defined as the electrical conductivity divided by amount-of-substance concentration.
. The molar and equivalent values are interconvertible through stoichiometric coefficient z. The customary unit is S cm 2 mol 1 ie Ω 1 cm 2 mol 1. Molar conductivity is defined as the conductance of that electrolytic solution that is kept between electrodes which are unit length apart.
G К A l. The equivalent conductivity refers to the normality of the solution rather than molarity. Molar Conductivity is defined as the Conductivity of the solution of an electrolyte divided by the Molar concentration of the electrolyte and so gauges the efficiency with which an allotted electrolyte conducts electricity in solution.
This table converts water conductivity and resistivity. 864-848-9569 Conductivity Chart of Liquids conductivity too low for mag. Offices at 1-866-404-5415 for assistance.
Arabic Chinese Simplified Dutch English French German Italian Portuguese Russian Spanish. The term limiting molar ionic conductivity is used according to lU-PAC recommendation rather than the formerly used limiting ionic equivalent conductivity. This is to say that Molar Conductivity is the conducting power of all the ions that are developed by.
Table 1 gives the molar electrical conductivity of the hydrohalogen acids at 25 C as a function of the concentration. Table 1 limiting Molar Ionic Conductivities of some Anions and Cations S cm mol at 25C. It is hoped that the following will provide a ready and reasonably accurate reference of conduc-tance values for the majority of electrolytes encoun-.
Conductivity or well-known as Specific Conductivity is the measurement of materials ability for conduction of electricity. The ultrasonic velocities u for the estimation of isentropic compressibility were measured using a pulse echo overlap technique. Ionic conductiVity and diffusion at infinite dilution Petr Vanysek This table gives the molar equivalent conductivity λ for com-mon ions at infinite dilution.
A supplementary list of other ionic mobilities is given in Table 2. Molar conductivities Λ M are normally determined using 1 10 3 M solutions of the complexes. If a particular chemical is not listed or if you would like application assistance with an electromagnetic flowmeter application please feel free to contact SmartMeasurement TM s US.
All values refer to aqueous solutions at 25 C. Here c symbolizes the molar concentration of the electrolyte in molL and z refers to the electrical charge. For very dilute solutions the molar electrical conductivity for any electrolyte of concentration c can be approximately calculated using the DebyeHückelOnsager equation.
K is the symbolic representation of it. Conductivity changes can frequently be useful for studying the reactions of metal complexes in solution. To calculate the conductivity of a solution you simply multiply the concentration of each ion in solution by its molar conductivity and charge then add these values for all ions in solution.
Molar heat capacity gases. The term limiting molar ionic conductivity is used according to lU-PAC recommendation rather than the formerly used limiting ionic equivalent conductivity. 228 rows Conductivity values displayed in yellow are questionable.
R ρ 1 A. As a result by definition G 1 R. Please contact the SmartMeasurement factory for assistance.
Where these differ from the values previously listed and incorporated in JPCalc the new updated values are now listed below. It also converts resistivity to conductivity and to parts per million or milligrams per liter ppm mgL. Much data has been generated in the past 100 years in this area but a comprehensive gath-ering of the information in a form useful to industry has been lacking1.
It accounts for the obvious fact that ions. The molar conductivity of OH-is 3-5 times the conductivity of other small anions. К 1 ρ.
Table 1 limiting Molar Ionic Conductivities of some Anions and Cations S cm mol at 25C. When the concentration of a solution reaches zero its molar conductivity is known as limiting molar conductivity. The molar and equivalent values are interconvertible through stoichiometric coefficient z.
Note that a number of values in the tables of Lange 2 and CRC 7 have been updated in their most recent editions currently listed in the references. Molar Conductivity of Selected Ions. CONTACT US 800 964-7035.
They have an area of cross-section A which is large enough to hold one mole of electrolyte. It also lists the diffusion coefficient D of the ion in dilute aqueous solution which is related to λ through the equation. S Siemens is the SI unit of conductance.
The molar conductivity Λ m is defined as the conductivity of a 1 molar aqueous solution placed between two plates electrodes 1 cm apart. Information about isotopes may be found in tables linked to the Periodic table. Typical ranges for different electrolyte types are listed in Table 28.
This table gives the molar equivalent electrical conductivity Λ at 25 C for some common electrolytes in aqueous solution at concentrations up to 01 M 01 molL.

Molar Conductance M Of Nacl And Kcl In Aqueous Polyvinyl Alcohol Download Table

Table 7 From Electrical Conductivity Of Electrolytes Found In Natural Waters From 5 To 90 C Semantic Scholar

The Limiting Molar Conductance L O Ion Pair Formation Constant K A Download Scientific Diagram

Limiting Molar Conductivities S Cm 2 Mol Of Equivalents In Download Table

Limiting Molar Conductance M For Nacl And Kcl In Aqueous Download Table

Equivalent Molar Conductivities And Corresponding Molarities Of The Download Table

Molar Conductivity M Of Cacl 2 At Different Temperatures In 0 50 Download Table

Molar Conductivity At Infinite Dilution 0 M Of Kcl And Cacl 2 At Download Table

Molar Conductivity M Of Cacl 2 At Different Temperatures In 0 50 Download Table

Equivalent Molar Conductivities And Corresponding Molarities Of The Download Table

Table 6 From Electrical Conductivity Of Electrolytes Found In Natural Waters From 5 To 90 C Semantic Scholar
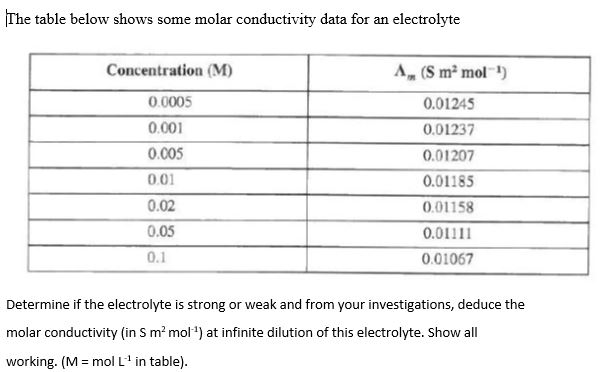
Solved The Table Below Shows Some Molar Conductivity Data Chegg Com

Molar Ionic Conductivities Of Some Mono Charged Ions Download Table
Ionic Species Molar Conductivity Assignment Help
Molar Conductivity Of Electrolytes Molar Conductivity Assignment Help
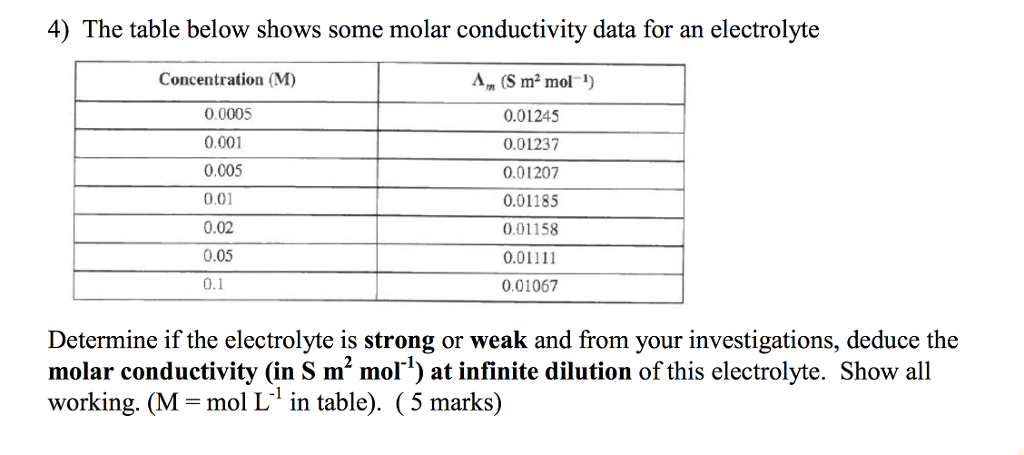
4 The Table Below Shows Some Molar Conductivity Data Chegg Com

Equivalent Molar Conductivities And Corresponding Molarities Of The Download Table
Conductometric And Thermodynamic Study Of Copper And Nickel Sulfate In Aqueous Methanol Systems

0 Response to "molar conductivity table"
Post a Comment